ISO 9001, the globally recognized quality management standard, is undergoing its planned revision. As a part of it the Draft International Standard (DIS) was issued recently. This update preserves the familiar framework of the 2015 version while integrating timely enhancements such as sustainability, ethics, and opportunity-based thinking. The changes reflect the evolving demands of modern business environments and aim to strengthen quality culture and organizational resilience.
Here is the summary of key proposed changes:
0. Introduction and Principles
2015:
- Seven Quality Management Principles: customer focus, leadership, engagement of people, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision making, and relationship management.
2025:
- Principles remain, but the process approach is even more strongly emphasized.
- Explicit connections to sustainable development and breakthrough change/innovation introduced.
- Much more emphasis on "opportunity-based thinking" alongside "risk-based thinking."
- Climate change and adaptation to dynamic external factors are mentioned as quality concerns.
3. Terms and Definitions
2025:
- Expanded and revised definitions reflecting clarity, digitalization, stakeholder, risk, and performance concepts.
- Interested party definition explicitly includes broader examples (e.g., society, competitors, unions, pressure groups).
- New or clarified definitions for "opportunity" and its relationship to risk.
4. Context of the Organization
2015:
- Organizations must consider external and internal issues and identify interested parties.
- Scope is determined based on those analyses.
2025:
- NEW: Requirement to determine if climate change is a relevant issue as part of context analysis (Clause 4.1).
- NEW: The requirements of interested parties may now include climate change.
5. Leadership
2025:
- NEW EXPLICIT ADDITION: Leadership must promote quality culture and ethical behaviour (5.1.1 i), not just demonstrate commitment.
- Customer focus clarified, now including regulatory/statutory requirements and a strengthened link to risk management.
- Top management must assign authority for "promotion of customer focus throughout the organization" and maintenance during changes.
6. Planning
2015:
- Focus on actions to address risks and opportunities, set quality objectives, plan changes.
2025:
- Expanded requirements:
- 6.1.2/6.1.3: Explicit addition of dedicated subclauses for actions to address risks (analyze, evaluate, proportionate actions, including after disruption) AND actions to address opportunities (adopt new practices, partnerships, technologies, etc.).
- Opportunity-based thinking is distinct, not just the absence of risk.
7. Support
2025:
- Maintains resource-related requirements.
- Additional emphasis on the need for persons necessary for effective operation, which may reflect remote/hybrid workplaces.
- Infrastructure: “hardware and software” now explicitly stated in examples.
- No significant reduction in documentation expectations, with support for new technologies, digitalization.
8. Operation
2025:
- Requirements are clarified and kept structurally the same, but there is a stronger link to risk and opportunity management throughout.
- Information for external providers includes clearer explanations of the extent/type of controls.
- Ongoing focus on changes to requirements for products and services and ensuring traceability.
9. Performance Evaluation
2025:
- Performance management remains key.
- Additional emphasis on evaluation of effectiveness of actions (especially for risks and opportunities).
- Explicit linkage to opportunity-based thinking in data evaluation and management reviews.
10. Improvement
2025:
- Continual improvement standard remains, with reinforced expectation of breakthrough changes, innovation, and proactive adaptation.
- Nonconformities and corrective action process are essentially unchanged but clarified.
ANNEXES
2025:
- Annex A: Provides further clarification, including on structure, terminology, and clauses (updated accordingly).
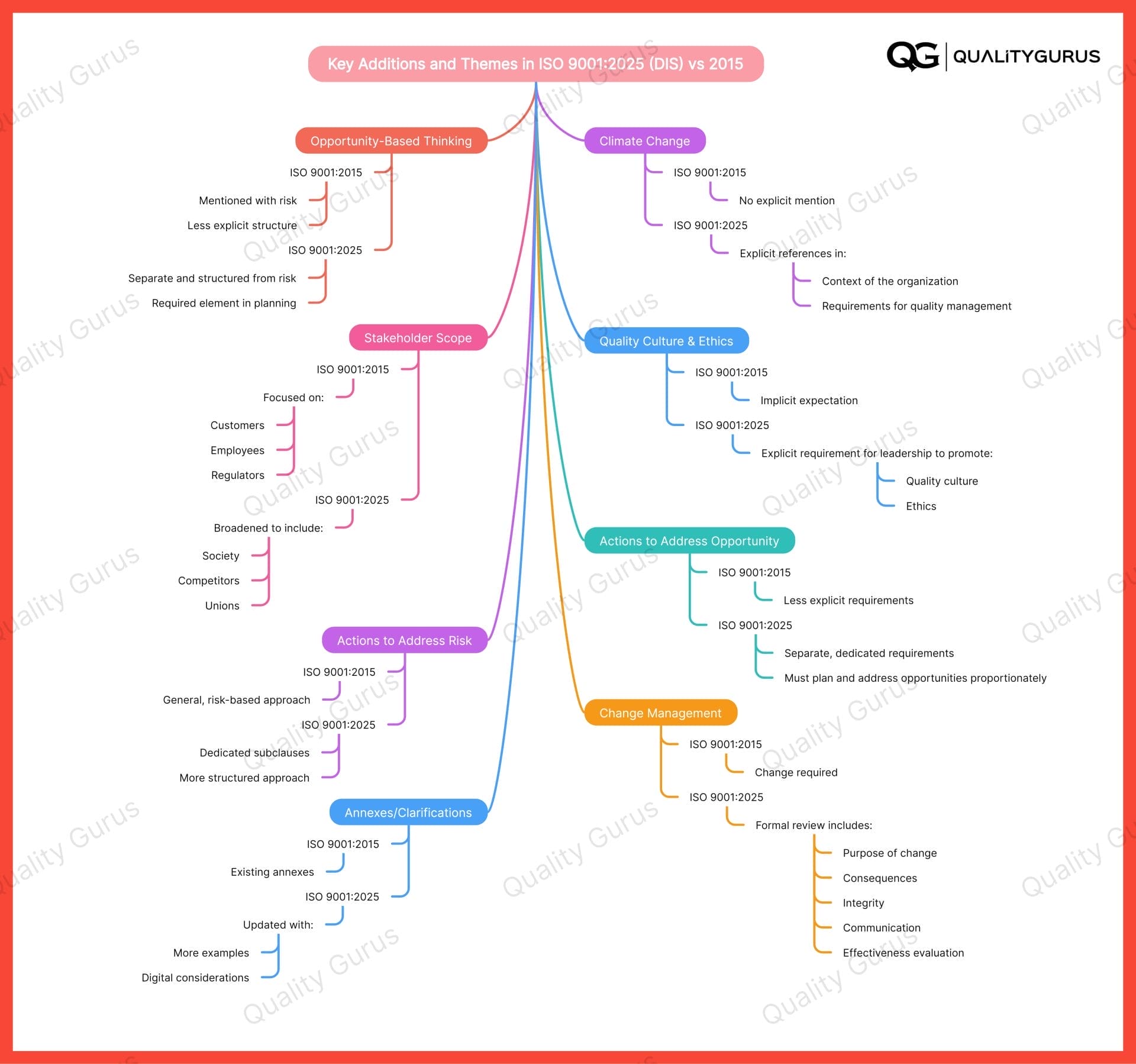
Key Additions and Themes in ISO 9001:2025 (DIS) vs 2015
| Area | ISO 9001:2015 | ISO 9001:2025 (DIS) |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change | Not explicitly mentioned | Explicitly referenced in context and requirements |
| Opportunity-based thinking | Paired with risk, less explicit | Separate, structured, required in planning |
| Quality culture & ethics | Implicit | Explicit requirement for leadership |
| Stakeholder scope | Customers, employees, regulators | Broader: e.g., society, competitors, unions |
| Digitalization | Not explicit | More examples and expectations (hardware/software, infrastructure) |
| Actions to address risk | Risk-based, general | Dedicated subclauses, more structured |
| Actions to address opportunity | Less explicit | Separate, dedicated, must be planned and addressed proportionately |
| Change management | Required | Requires formal review of purpose, consequences, integrity, communication, evaluation of effectiveness |
| Annexes/Clarifications | Existing | Updated with more examples, digital considerations |
Conclusion
The ISO 9001:2025 DIS represents a thoughtful evolution of the 2015 standard rather than a radical overhaul. It reinforces core aspects of risk-based thinking while embedding new priorities like climate change, stakeholder inclusivity, and ethical leadership.